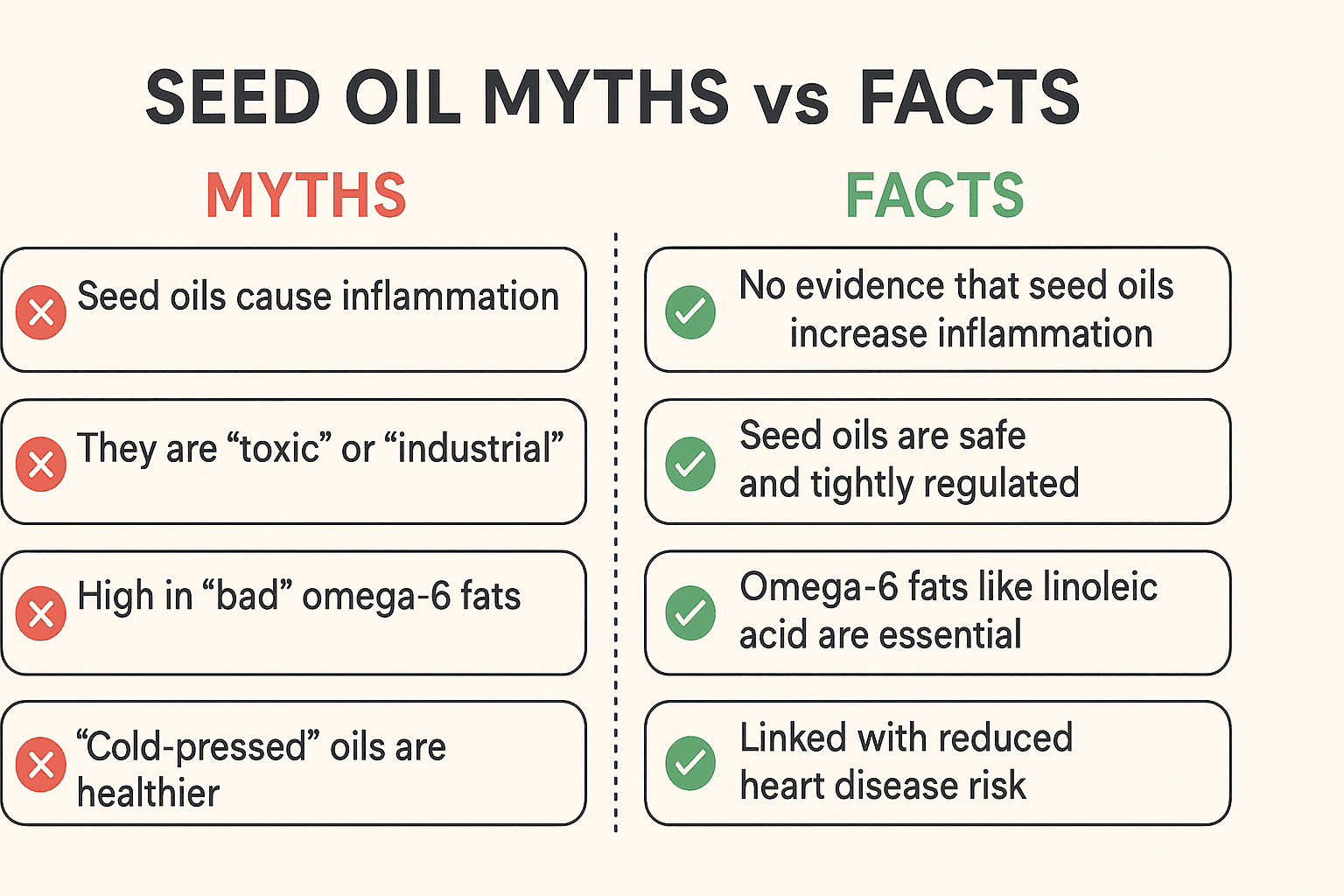
The Viral Claim
What Inflammation Actually Means
Inflammation is the body’s immune response — an essential defense mechanism.
Acute inflammation heals wounds and fights infection.
Chronic inflammation, triggered by smoking, obesity, or inactivity, contributes to diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
The key question: Do seed oils like sunflower oil promote chronic inflammation?
Understanding Linoleic Acid (Omega-6 Fat)
Sunflower oil is rich in linoleic acid (LA), an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Despite online fear, LA is essential — our bodies can’t make it, and it’s required for cell membranes, brain function, and skin barrier health.
Recommended daily intake: 12–17 g for adults (NIH).
Balanced omega-6 : omega-3 ratio (ideally < 10 : 1) supports normal physiology.
What the Research Actually Shows
Human trials and reviews find no evidence that dietary LA or sunflower oil increases inflammation markers:
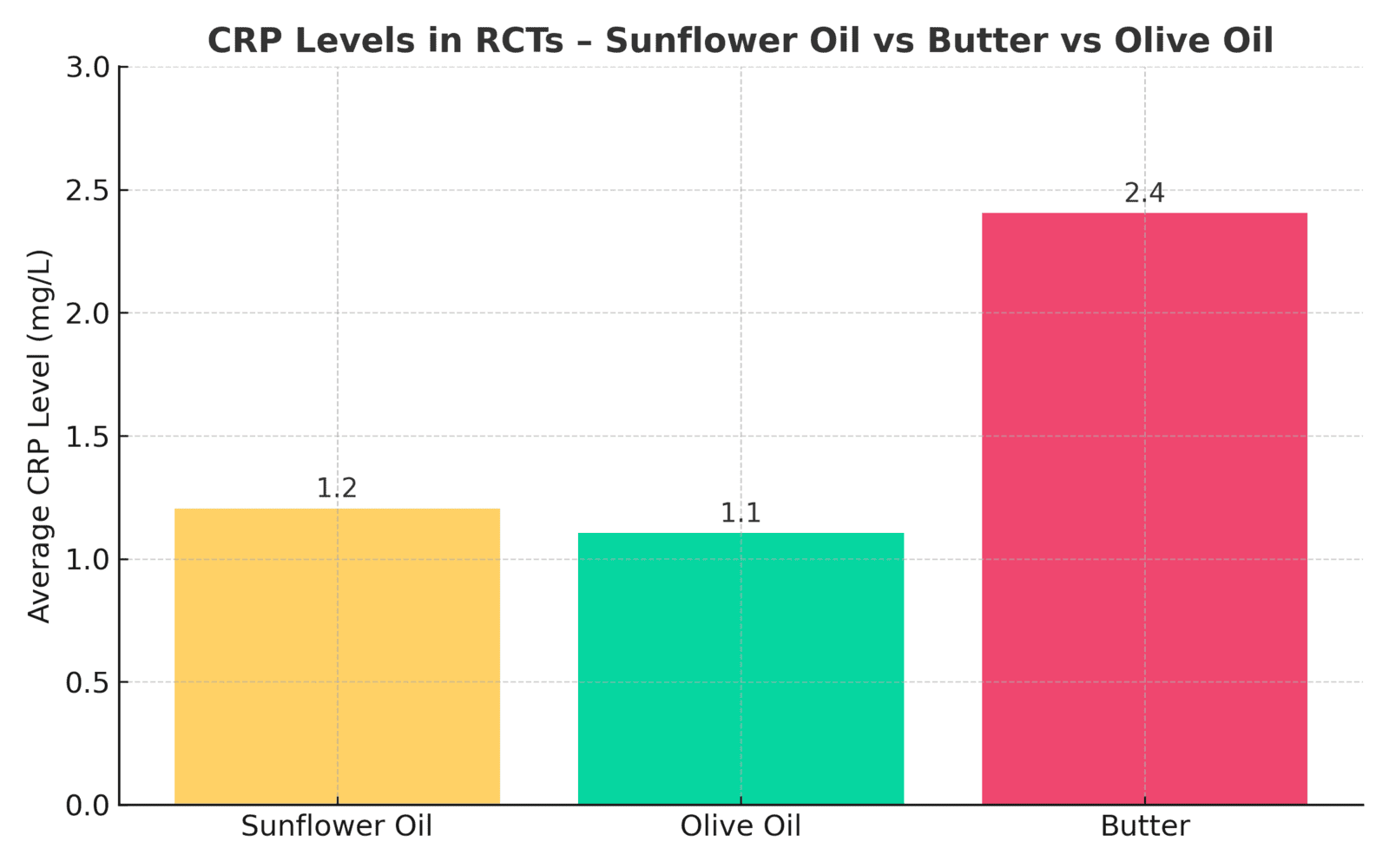
A 2019 systematic review of 30 randomized controlled trials (Johnson et al., Am J Clin Nutr) found no rise in C-reactive protein (CRP) or IL-6 when subjects consumed sunflower or soybean oil versus olive oil.
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health concludes: “Replacing saturated fats with polyunsaturated fats, such as those in sunflower oil, reduces heart disease risk and does not promote inflammation.”
Plasma linoleic acid levels in large population studies correlate with lower risk of chronic inflammation and metabolic syndrome (Wu et al., Circulation 2021).
✅ Bottom line: Consuming moderate amounts of sunflower oil as part of a balanced diet reduces rather than increases inflammation risk.
Why the Internet Got It Wrong
Social media thrives on outrage and simplicity.
Complex biochemistry gets reduced to “good vs bad.”
People confuse oxidation in the lab with metabolism in the body.
Reused or overheated oils can produce aldehydes — but that’s about cooking behavior, not the oil itself.
Misinformation spreads because fear drives clicks — and nuance doesn’t go viral.
How to Keep Sunflower Oil Truly Anti-Inflammatory
You can maximize benefits with smart habits:
Avoid repeated frying — oxidation increases only with multiple reheats.
Store properly — sealed bottle, dark and cool place.
Pair with antioxidants — herbs, garlic, or lemon enhance oxidative balance.
Keep diet balanced — include omega-3 sources (flaxseed, salmon, walnuts).
Key Takeaway
Science verdict: Sunflower oil does not cause inflammation.
When used correctly, it supports heart health and provides essential fats your body needs every day.
References
National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements — Linoleic Acid Fact Sheet
Johnson GH et al., Am J Clin Nutr 2019 — Meta-Analysis on Omega-6 PUFAs and Inflammation
Wu JHY et al., Circulation 2021 — Plasma Linoleic Acid and Cardiometabolic Risk
Cook Smarter — Not Louder.
Bring science-backed flavor to your kitchen with Westa Pure Sunflower Oil — premium, non-GMO, FDA-registered, and crafted for both health and taste.

